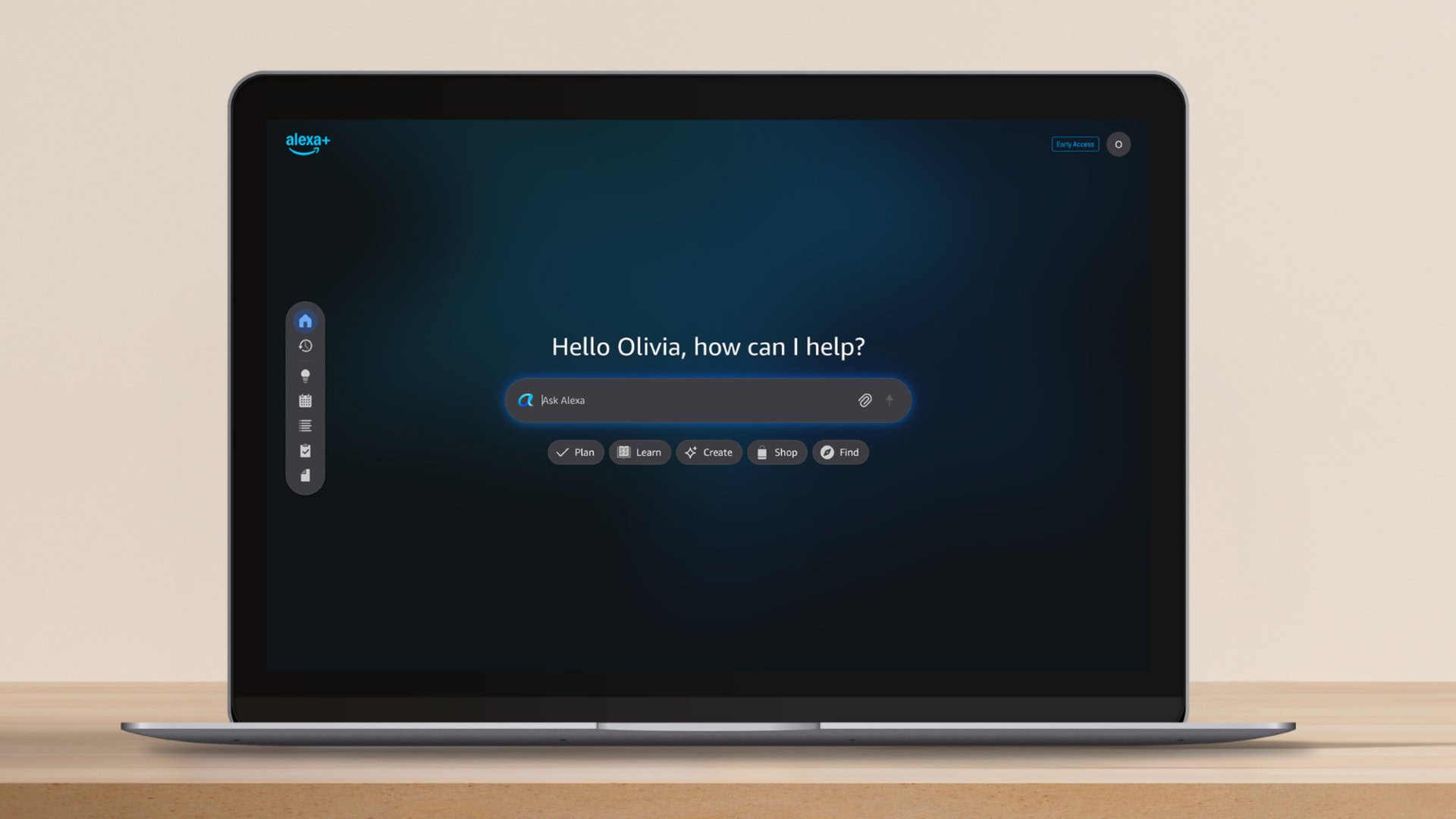
The digital assistant landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the rapid maturation of large language models (LLMs) and generative AI capabilities. For nearly a decade, Amazon’s Alexa has maintained a formidable presence in the smart home ecosystem, primarily through dedicated echo devices and voice interaction. However, the evolution to "Alexa Plus"—the company’s significantly upgraded, more capable AI—has highlighted the limitations of a purely voice-first, device-centric deployment strategy. This strategic gap is now being decisively addressed with the introduction of a dedicated web portal for Alexa Plus, effectively transplanting the sophisticated assistant directly into the user’s browser environment.
This development, announced recently, signals a critical pivot for Amazon, moving Alexa from a peripheral appliance to a central, platform-agnostic productivity tool. Nine months after the initial unveiling of Alexa Plus, which promised substantial advancements in reasoning, content creation, and complex task execution, its absence from the desktop and laptop interface was a glaring omission in the broader AI race. Competitors, notably Google with Gemini (accessible via Gemini.Google.com), have aggressively established web-based presences to capture users working outside the confines of dedicated smart speakers or mobile applications. Amazon’s move to launch Alexa.com directly mirrors this industry trend, aiming to capture the substantial productivity workflow that occurs within web browsers.
The immediate benefit for existing Alexa Plus early access customers is straightforward: ubiquitous access. Users can now engage with the advanced assistant for tasks ranging from intricate informational retrieval and sophisticated content drafting to managing personal logistics like scheduling and reservations, all without needing a physical device nearby or relying solely on a mobile application. This transition dramatically widens the utility envelope of Alexa Plus, positioning it not just as a home controller but as a genuine digital colleague.
A key component of this web integration, as highlighted by Amazon, is the commitment to continuity. The platform assures that all established conversational histories, learned preferences, and deep personalization settings—the accumulated digital context built up over months of use on other devices—are seamlessly migrated to the web interface. This solves a major pain point in multi-device AI ecosystems: the need for users to repeatedly train or reconfigure their assistant profile across different hardware or software silos. For the user, this means a consistent, context-aware experience whether they are speaking commands to an Echo Show in the kitchen or typing prompts into Alexa.com at their desk.
Beyond standard generative AI functionalities, the integration of smart home control represents a significant architectural achievement in this web deployment. The Alexa ecosystem’s core strength has always been its dominance in connected living spaces. The web portal is engineered to bridge the digital and physical worlds instantly. Users can transition fluidly from asking Alexa Plus to summarize a complex financial report to issuing commands to their home infrastructure—checking the status of a front door camera, adjusting ambient lighting levels, or modifying the smart thermostat settings—all within the same browser window. This capability is further streamlined by a dedicated sidebar, designed as a quick-access dashboard for frequently used routines and favored smart home controls, enhancing operational efficiency.
The Broader Context: The AI Interface Wars
To fully appreciate the significance of Alexa.com, one must understand the competitive dynamics that have defined the AI assistant market over the past two years. Initially, assistants like Alexa and Google Assistant were primarily positioned as command-and-control layers for smart devices, excelling at simple queries, timers, and music playback. The advent of advanced generative AI, however, has forced a complete re-evaluation of what an "assistant" means. It is no longer just about retrieval; it is about creation, synthesis, and complex problem-solving.
Amazon’s initial strategy for Alexa Plus focused heavily on embedding these new cognitive capabilities into its existing hardware footprint—Echo devices, Fire TV, and specific automotive integrations. While this leveraged their installed base, it created a dependency on Amazon’s hardware ecosystem. In contrast, rivals understood that true market saturation in the productivity sector requires a browser-based presence. Microsoft has aggressively integrated Copilot across Windows and the Edge browser, and Google has made Gemini foundational to its web services. By launching Alexa.com, Amazon is finally establishing parity in interface accessibility, ensuring that Alexa Plus is not left behind as the primary locus of digital work shifts back to the desktop environment.
This move reflects a recognition that the modern digital worker splits their time between dedicated apps and browser tabs. If Alexa Plus cannot service complex workflow requests (like drafting detailed email responses or analyzing spreadsheet data) directly within the browser environment where much of that work occurs, its perceived value proposition diminishes against more accessible rivals.
Industry Implications: Platform Neutrality vs. Ecosystem Lock-in
The introduction of a robust, web-accessible Alexa Plus has significant ramifications for the broader technology industry. For years, Amazon successfully utilized its hardware (Echo speakers) as a powerful mechanism for ecosystem lock-in. Users invested in Amazon’s hardware ecosystem because Alexa was the best way to manage their connected home devices, often creating friction for users attempting to integrate competing platforms like Apple HomeKit or Google Home.
The web portal presents a nuanced challenge to this strategy. On one hand, it democratizes access to Alexa Plus’s advanced AI capabilities, potentially drawing in users who might have avoided the dedicated hardware but are attracted to the underlying AI engine’s performance. This broadens Amazon’s potential user base beyond the traditional smart home enthusiast.
On the other hand, by offering core generative AI features via a platform-neutral web interface, Amazon slightly dilutes the necessity of owning an Echo device solely for conversational AI tasks. This is a calculated risk. Amazon is betting that the unique, seamless integration of Alexa Plus with their vast e-commerce infrastructure and the deep smart home control will still incentivize hardware purchases, even if the basic chat interface is available everywhere. It shifts the value proposition from "access to Alexa" to "superior integration with the Amazon ecosystem."
Furthermore, this move puts pressure on smaller smart home platforms. If Alexa Plus on the web can reliably manage complex scenes and diagnostics across a wide array of third-party devices, it solidifies Amazon’s position as the central operating system for the digital home, irrespective of the device the user is currently operating.
Expert Analysis: The Technical Merits of Web Integration
From a technical perspective, porting a sophisticated multimodal assistant like Alexa Plus to the web involves overcoming several engineering hurdles. The primary challenge is maintaining low latency for voice interactions while ensuring robust security for sensitive smart home commands.
The seamless transfer of conversational context mentioned by Amazon suggests a cloud-native architecture where the session state is decoupled from the front-end client. This allows the user to begin a complex query via voice on a mobile device, pause, and resume the exact thread via text input on the web interface without error. This level of session persistence is crucial for productivity AI tools, where multi-step reasoning chains are common.
The smart home integration via the web interface is particularly noteworthy. Typically, direct device control requires local network access or specific proprietary protocols optimized for dedicated hardware. Executing commands like "unlock the door" through a web browser necessitates stringent security protocols, likely involving encrypted authentication tokens tied to the user’s Amazon account, ensuring that only an authenticated user within the specific browser session can trigger critical security actions. The success of this feature hinges on minimizing the latency between the web command issuance and the physical device execution, a factor where voice-optimized hardware usually holds an advantage. If the web portal can achieve near-instantaneous response times for home control, it validates the heavy investment in unifying the platform architecture.
Future Trajectories and Unfolding Trends
The launch of Alexa.com is not an endpoint; it is a clear indication of where Amazon sees the future of ambient computing leading. We can anticipate several related developments stemming from this foundational web deployment:
-
Deeper Generative Productivity: Expect Alexa Plus on the web to rapidly integrate more deeply with Amazon’s business software portfolio, particularly in areas related to e-commerce logistics, AWS management queries (for developers), and potentially leveraging document analysis features directly within the browser context. The web interface provides the necessary scaffolding for handling rich text and file uploads that are awkward or impossible via voice alone.
-
Multimodality Expansion: While the initial announcement focuses on text and voice interaction, the web platform is inherently better suited for visual feedback. Future iterations will likely feature richer graphical outputs for data visualization, complex scheduling interfaces, and interactive walkthroughs for troubleshooting smart home setups, moving beyond simple text replies.
-
Developer Ecosystem Integration: A unified web presence simplifies the process for third-party developers building "Skills." Developers can now test and deploy web-based front-ends or visualizations that interact with their Alexa services, expanding the usability of Skills beyond the confines of Echo Show displays or mobile apps.
-
The Convergence of Commerce and AI: Amazon’s primary long-term goal remains optimizing the customer journey toward purchase. With Alexa Plus fully integrated into the browser environment—the place where research, price comparison, and final transactions occur—Amazon gains another powerful, passive touchpoint to influence buying behavior through contextual recommendations powered by the advanced AI.
In conclusion, the debut of the Alexa Plus web portal marks a necessary, strategic evolution for Amazon. It addresses the structural limitations of a voice-first approach in the age of advanced generative AI, ensuring that Alexa remains competitive not just in the living room, but across the entire spectrum of digital productivity. It is a declaration that Alexa is evolving from a smart home accessory into a comprehensive, cross-platform digital intelligence layer. The immediate access for early adopters suggests Amazon is keen to gather rapid feedback on web-specific interaction patterns before a wider rollout, solidifying the assistant’s relevance for the next generation of computing.